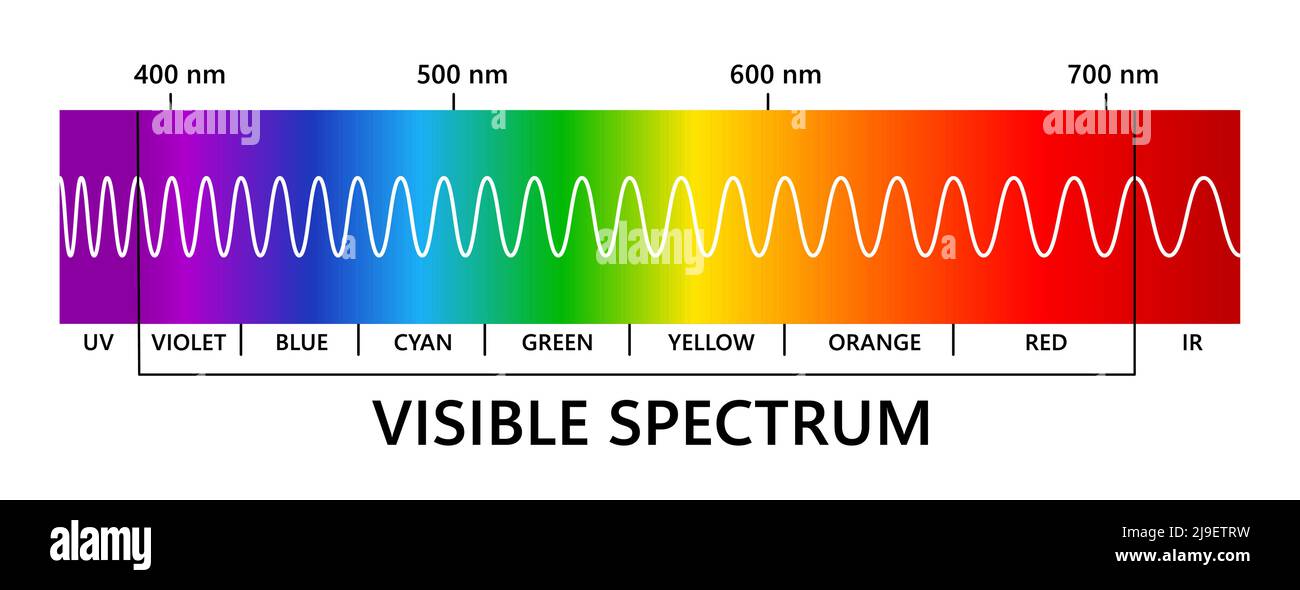
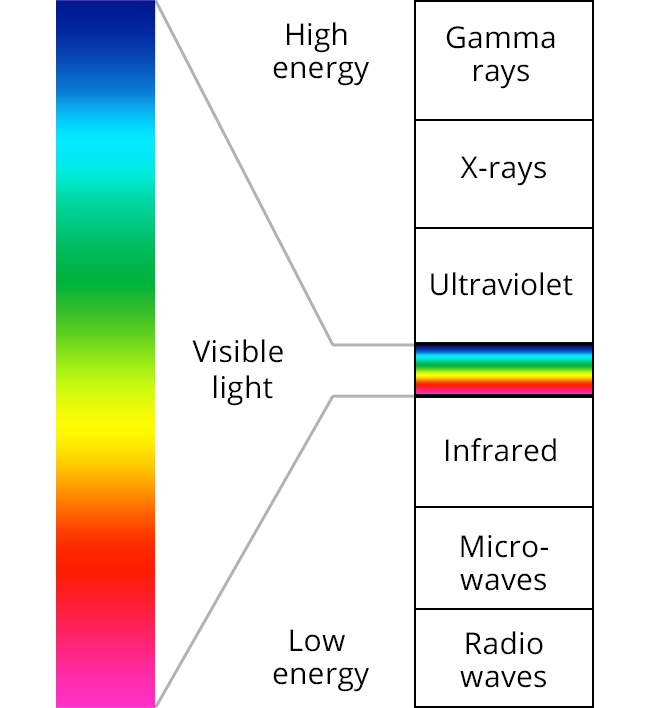
Visible light spectrum, infared and ultraviolet. Light wavelength
UV/Vis absorption spectra also involve radiation from the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum with wavelengths between 400 and 800 nm. A diagram highlighting the various kinds of electronic excitation that may occur in organic molecules is shown below.

What is ultraviolet radiation? Definition and examples
Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation is emitted by the Sun and are the reason skin tans and burns. "Hot" objects in space emit UV radiation as well. X-ray: A dentist uses X-rays to image your teeth, and airport security uses them to see through your bag. Hot gases in the Universe also emit X-rays.
SPF
UV (Ultraviolet) Light refers to the region of the electromagnetic spectrum between visible light and X-rays, with a wavelength falling between 400 and 10 nanometers. This electromagnetic radiation is not visible to the human eye, because it has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency than the light our brain perceives as images.
The ABC's of Ultraviolet Radiation
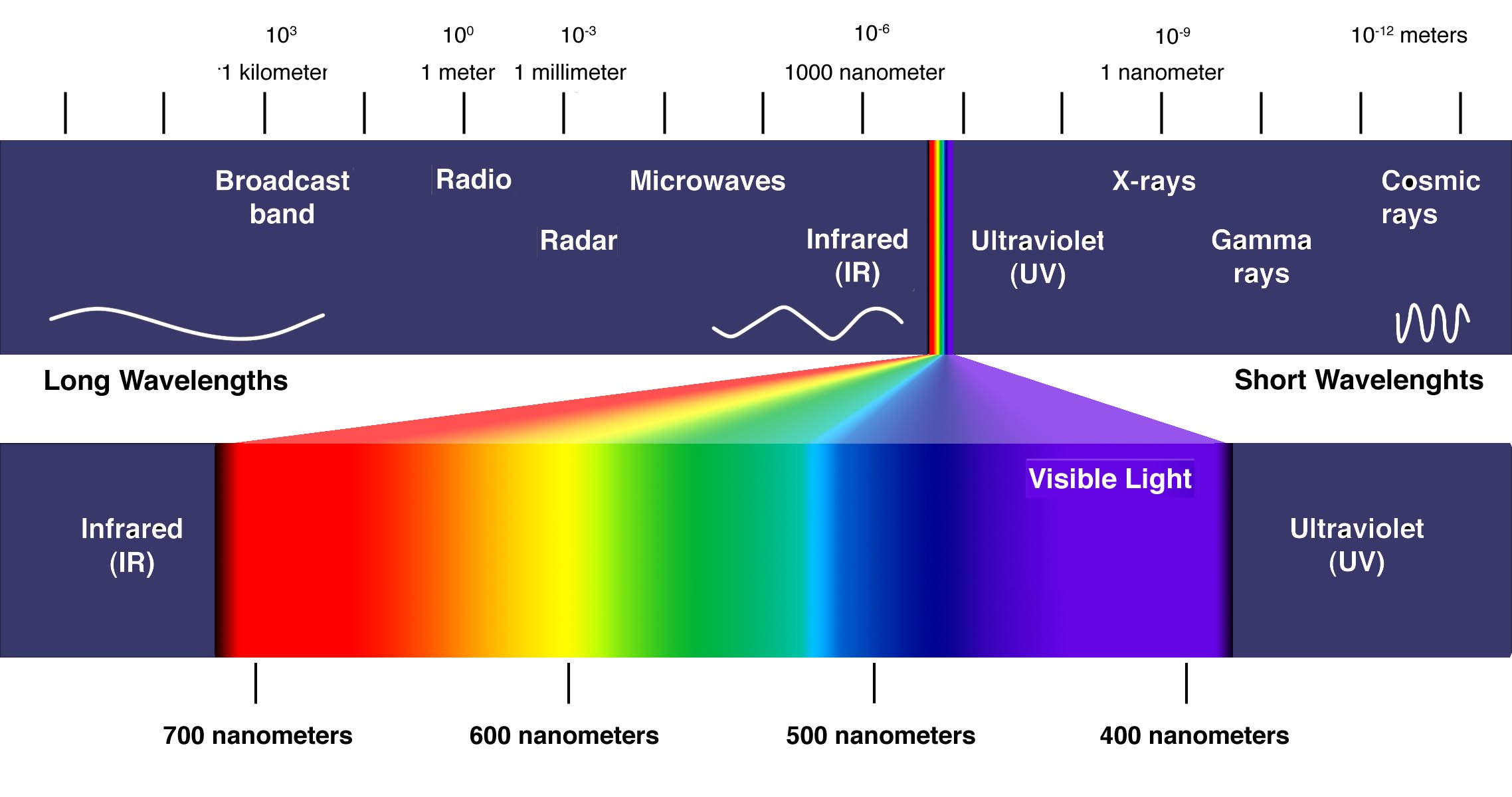
A diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths, as well as the equivalent blackbody temperature The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength.
UV curing science
Optical radiation is radiant energy within a broad region of the electromagnetic spectrum that includes ultraviolet (UV), visible (light) and infrared radiation. Ultraviolet radiation (UVR) is characterized by wavelengths between 10 and 400 nm—bordered on the one side by x rays and on the other by visible light (Fig. 1). Solar radiation is largely optical radiation, although ionizing.

Spectrum of ultraviolet (UV) light and wavelengthdependent
While interaction with infrared light causes molecules to undergo vibrational transitions, the shorter wavelength, higher energy radiation in the UV (200-400 nm) and visible (400-700 nm) range of the electromagnetic spectrum causes many organic molecules to undergo electronic transitions.What this means is that when the energy from UV or visible light is absorbed by a molecule, one of its.
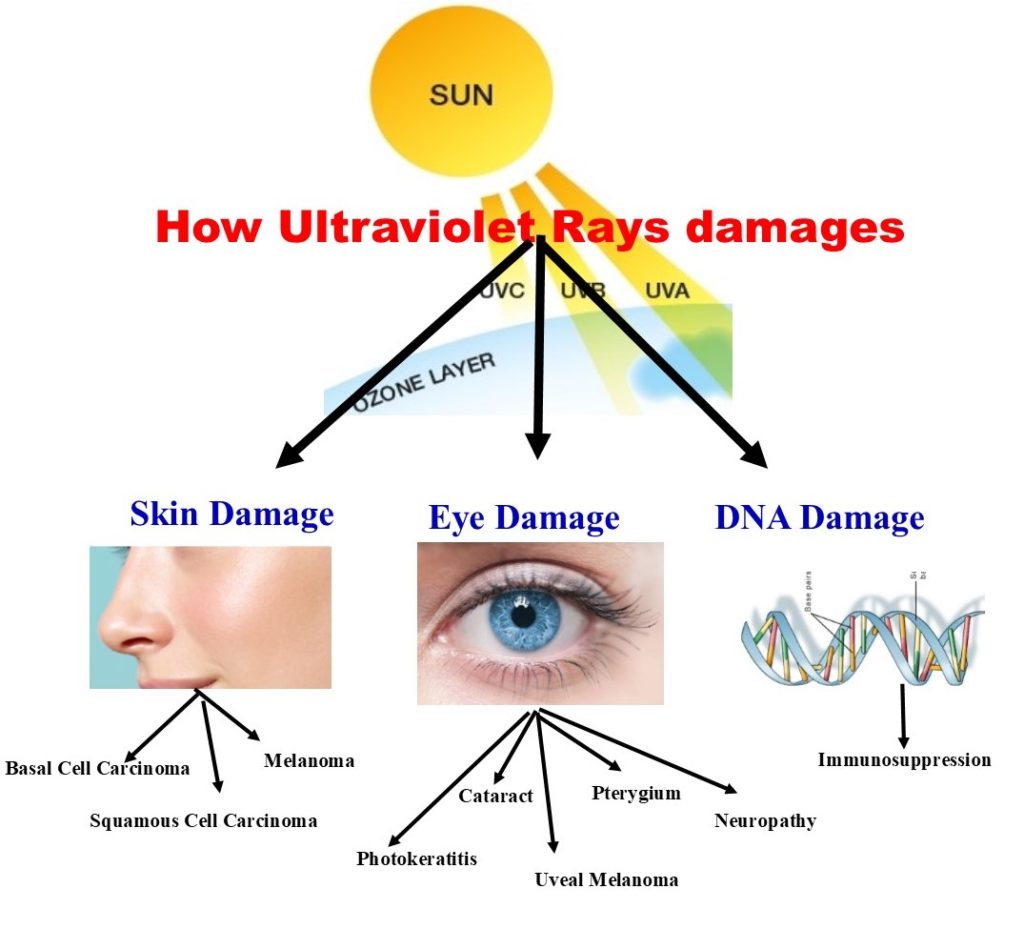
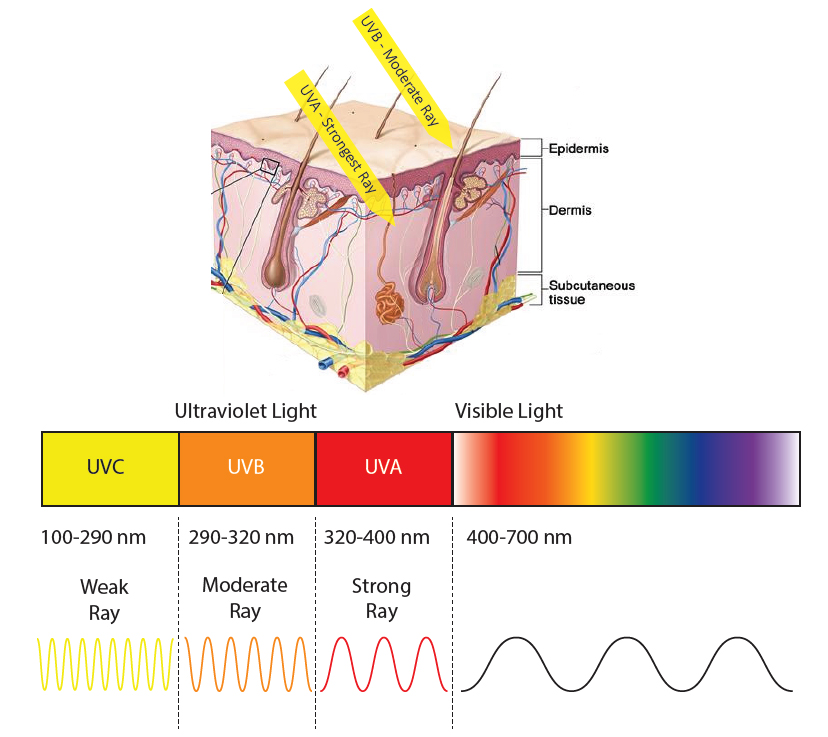
How Ultraviolet rays damagesskin, eyes and DNA? g
Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, that is, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, corresponding to photon energies from 3 eV to 124 eV (1 eV = 1.6e-19 J; EM radiation with frequencies higher than those of visible light are often expressed in terms of energy rather than frequency). It is so-named because the.

How Extreme Ultraviolet Light Helps Give Us Smarter Smartphones and
What Is UV Light? UV light (ultraviolet light) has a wavelength between 10 and 400 nm that is shorter than the visible light but longer than the X-rays and is a type of electromagnetic radiation. These are present in sunlight and contribute 10% of the total light from the sun. UV rays Types of UV light

How many types of UV radiation are there and what’s the difference
Overview Ultraviolet line spectrum measurements ( spectroscopy) are used to discern the chemical composition, densities, and temperatures of the interstellar medium, and the temperature and composition of hot young stars. UV observations can also provide essential information about the evolution of galaxies.

Ultraviolet Waves Diagram
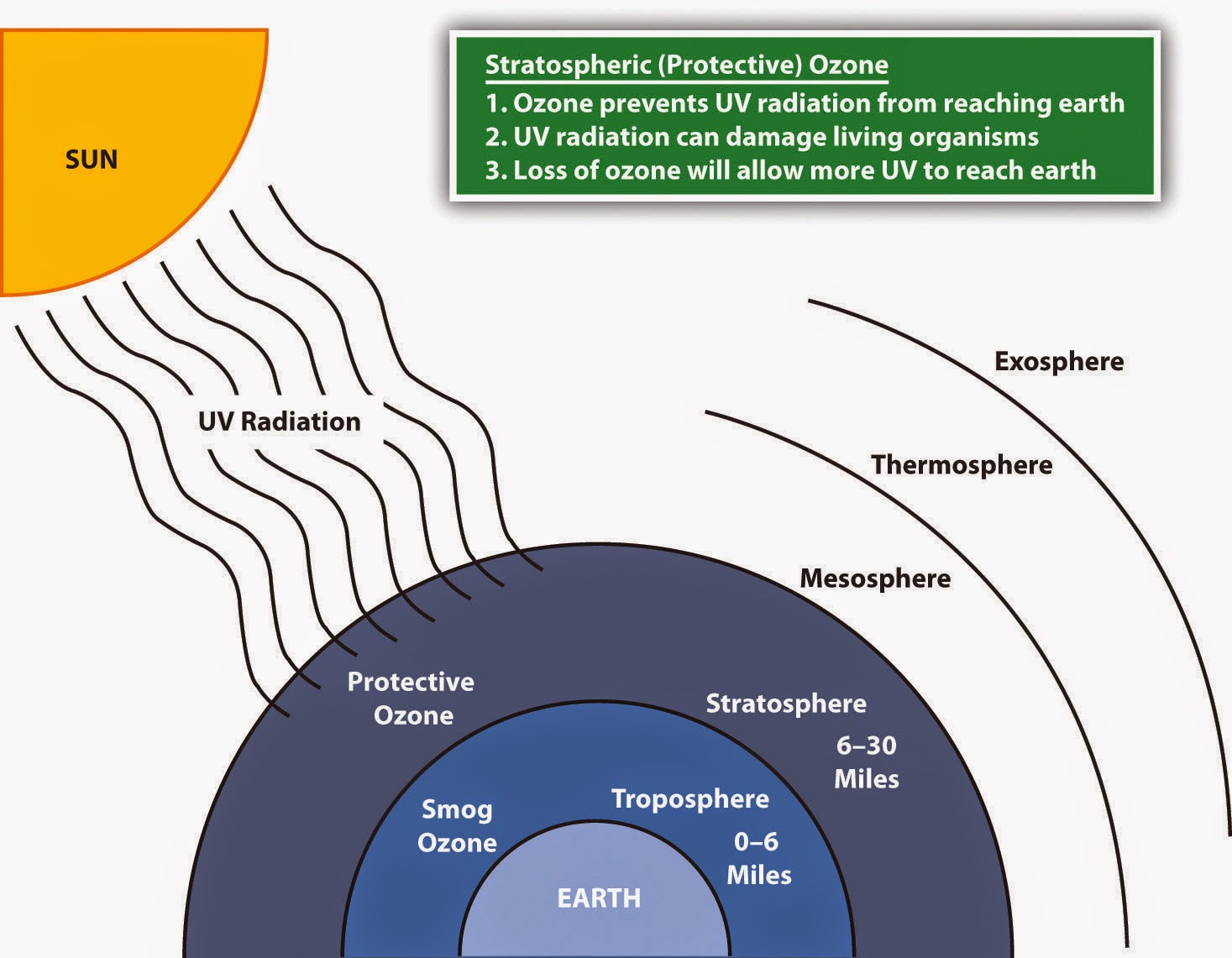
Since the Earth's atmosphere absorbs much of the high-energy ultraviolet radiation, scientists use data from satellites positioned above the atmosphere, in orbit around the Earth, to sense UV radiation coming from our Sun and other astronomical objects.

Understanding Ultraviolet UV Radiation and its Effects YouTube
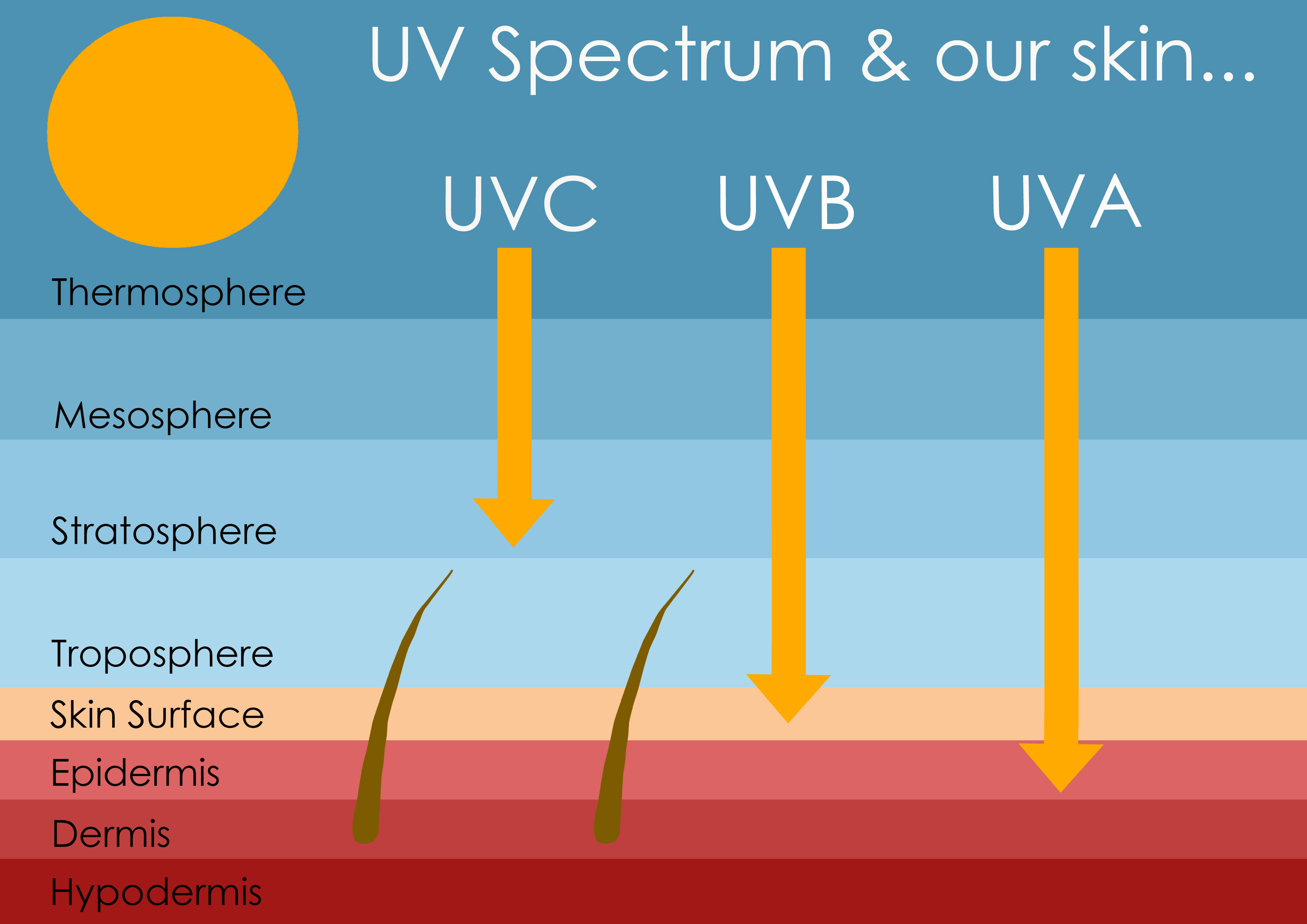
Visibility Ultraviolet rays are usually invisible to most humans. The lens of the human eye blocks most radiation in the wavelength range of 300-400 nm; shorter wavelengths are blocked by the cornea. [6] Humans also lack color receptor adaptations for ultraviolet rays.
Ultraviolet radiation and sunglasses How to protect your eyes
Ultraviolet radiation lies between visible light and X-rays along the electromagnetic spectrum. UV "light" spans a range of wavelengths between about 10 and 400 nanometers. The wavelength of violet light is around 400 nanometers (or 4,000 Å). Ultraviolet radiation oscillates at rates between about 800 terahertz (THz or 10 12 hertz) and 30,000 THz.

Diagram of ultraviolet rays and sunscreen Stock Vector Image by ©mug5
Advanced; Basic; The Electromagnetic Spectrum. As it was explained in the Introductory Article on the Electromagnetic Spectrum, electromagnetic radiation can be described as a stream of photons, each traveling in a wave-like pattern, carrying energy and moving at the speed of light.In that section, it was pointed out that the only difference between radio waves, visible light and gamma rays is.
Science online Examples and some technological applications of
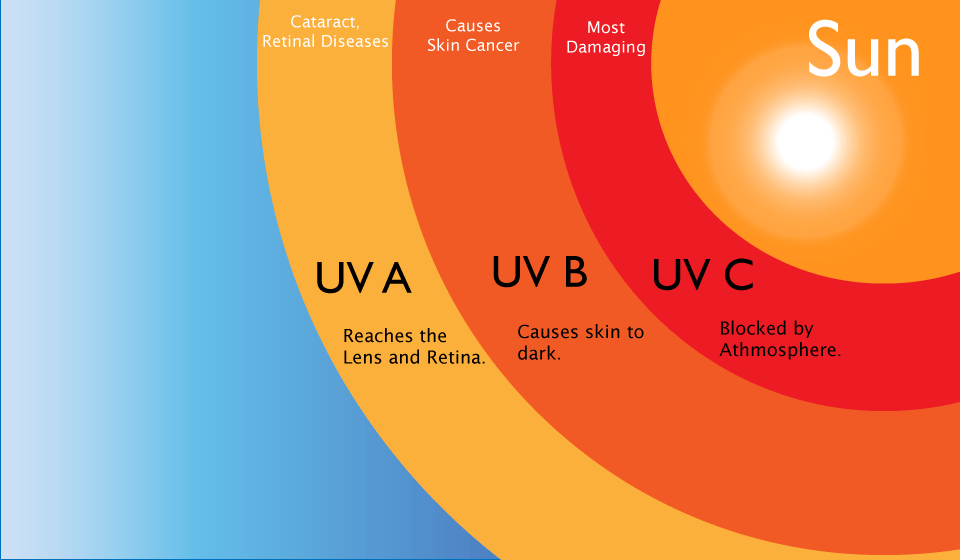
UVA (315-400 nm) UVB (280-315 nm) UVC (100-280 nm). Short-wavelength UVC is the most damaging type of UV radiation. However, it is completely filtered by the atmosphere and does not reach the earth's surface. Medium-wavelength UVB is very biologically active but cannot penetrate beyond the superficial skin layers.
Understanding Acuvue Contacts and Ultraviolet Light
Electromagnetic radiation is one of the many ways that energy travels through space. The heat from a burning fire, the light from the sun, the X-rays used by your doctor, as well as the energy used to cook food in a microwave are all forms of electromagnetic radiation. While these forms of energy might seem quite different from one another.
Effects Of Ultraviolet Radiation What is Ultraviolet Radiation
ultraviolet telescope, telescope used to examine the ultraviolet portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, between the portion seen as visible light and the portion occupied by X-rays. Ultraviolet radiation has wavelengths of about 400 nanometres (nm) on the visible-light side and about 10 nm on the X-ray side. Earth 's stratospheric ozone.